What it means?
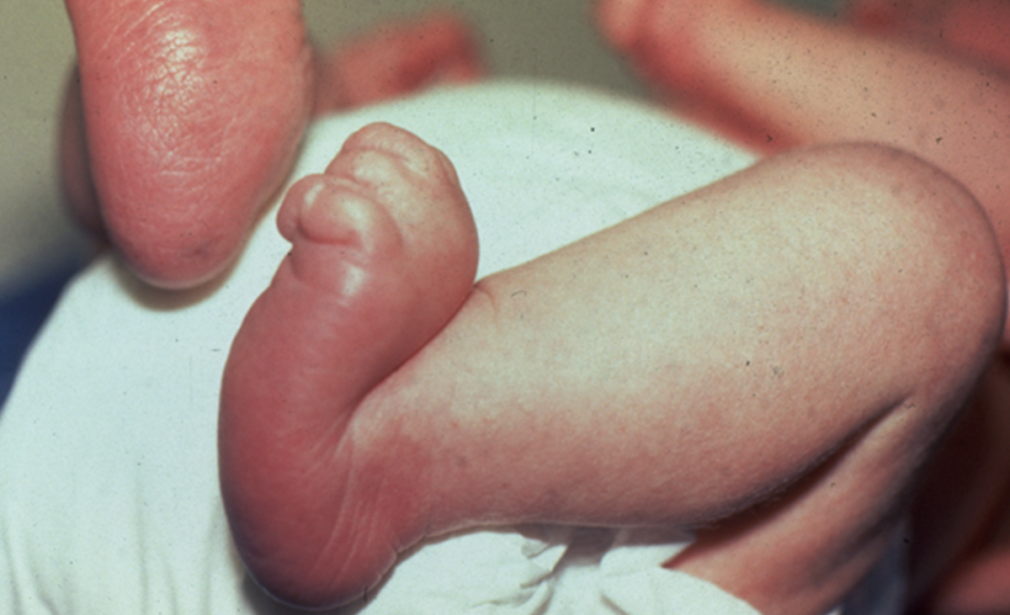
The talus is small bone in the ankle which is present between shin bone (tibia and fibula) above and heel bone (calcaneum) below it. Normally, the talus will lie in line with the toes but in vertical talus, the talus will be pointing down towards the ground
What causes it?
Wrong position of the talus that is pointing downwards, and the bones lying in front of it will now sit on top of talus make the foot bend back upward. As result of this positioning, normal foot arch will be absent and foot under surface looks curved hence known as Rocker Bottom Foot
Vertical talus can occur alone or it can be associated with other conditions like arthrogryposis, spina bifida or other neurological conditions
Less severe form of this deformity is known as Oblique talus in which the talus is wrong positioned that is downwards during weight bearing but realign with the toes normally when foot pointed down.
How child will present like?
- Newborn baby will have no arch of foot
- Under surface of the feet will be curved like rocker bottom chair
- Foot will be rigid and movements of the foot will be restricted
- Baby can have problems in other joints too if vertical talus is associated with other condition like Arthrogryposis
What are the tests required?
- X-ray of the foot pointing downwards required in order to determine whether the bones in front of talus line up properly or stuck on top of talus
- If the bones stuck on the top of talus is Vertical Talus and if it lines up properly with talus means Oblique Talus
What are the treatment options?
Here the aim of treatment is to provide painless, stable functional foot that fits in shoes comfortably which can be achieved serial casting and followed by surgical correction
Initially baby with vertical talus can be treated with serial stretching and casting which helps to improve the flexibility of the foot. Casting helps to gradually stretch out the soft tissue and correct the deformity without causing too much pressure. Baby needs weekly cast change for multiple weeks until correction of deformity.
After serial casting, some deformity persist or foot is rigid fails to get corrected after casting needs to undergo surgical correction. If only some deformity present after casting limited surgery enough to get talus and other bones alignment. If foot remains rigid and deformed, more extensive surgery is required to achieve corrected foot position.
The aim of the surgery is to align the talus with other foot bones and make the foot flexible and functional. In order to achieve this tight tendons and ligaments were lengthened which will allow the bones to be moved and aligned in position. The bones were fixed in aligned position with k wires and cast. The wires can be removed in Out patient department after 4 to 6 weeks.
A special shoe or brace will be recommended in order to prevent recurrence. Baby need to be kept under regular follow up for few years to assess any recurrence and foot growth
What will be outcome?
- Diagnosed early and treated by serial casting followed by surgery can result in painless, stable, functional foot
- If left untreated, the foot will remain in deformed position. As child begins to walk over the deformed foot results in painful callosity, skin breakdown which makes the child difficult to wear shoes and walk
- Need to be followed regularly in order to detect any form of recurrence at the earliest and treat accordingly